# Web Sockets
The WebSockets module provides an implementation of the WebSockets protocol for WebSockets clients and servers. It mirrors the Qt CPP module. It allows sending a string and binary messages using a full duplex communication channel. A WebSocket is normally established by making an HTTP connection to the server and the server then “upgrades” the connection to a WebSocket connection.
In Qt/QML you can also simply use the WebSocket and WebSocketServer objects to creates direct WebSocket connection. The WebSocket protocol uses the “ws” URL schema or “wss” for a secure connection.
You can use the web socket qml module by importing it first.
import QtWebSockets
WebSocket {
id: socket
}
# WS Server
You can easily create your own WS server using the C++ part of the Qt WebSocket or use a different WS implementation, which I find very interesting. It is interesting because it allows connecting the amazing rendering quality of QML with the great expanding web application servers. In this example, we will use a Node JS based web socket server using the ws (opens new window) module. For this, you first need to install node js (opens new window). Then, create a ws_server folder and install the ws package using the node package manager (npm).
The code shall create a simple echo server in NodeJS to echo our messages back to our QML client.
cd ws_server
npm install ws
The npm tool downloads and installs the ws package and dependencies into your local folder.
A server.js file will be our server implementation. The server code will create a web socket server on port 3000 and listens to an incoming connection. On an incoming connection, it will send out a greeting and waits for client messages. Each message a client sends on a socket will be sent back to the client.
const WebSocketServer = require('ws').Server
const server = new WebSocketServer({ port : 3000 })
server.on('connection', function(socket) {
console.log('client connected')
socket.on('message', function(msg) {
console.log('Message: %s', msg)
socket.send(msg.toString())
});
socket.send('Welcome to Awesome Chat')
});
console.log('listening on port ' + server.options.port)You need to get used to the notation of JavaScript and the function callbacks.
# WS Client
On the client side, we need a list view to display the messages and a TextInput for the user to enter a new chat message.
We will use a label with white color in the example.
// Label.qml
import QtQuick
Text {
color: '#fff'
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignLeft
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
}Our chat view is a list view, where the text is appended to a list model. Each entry is displayed using a row of prefix and message label. We use a cell width cw factor to split the with into 24 columns.
// ChatView.qml
import QtQuick
ListView {
id: root
width: 100
height: 62
model: ListModel {}
function append(prefix, message) {
model.append({prefix: prefix, message: message})
}
delegate: Row {
id: delegate
required property var model
property real cw: width / 24
width: root.width
height: 18
Label {
width: delegate.cw * 1
height: parent.height
text: delegate.model.prefix
}
Label {
width: delegate.cw * 23
height: parent.height
text: delegate.model.message
}
}
}The chat input is just a simple text input wrapped with a colored border.
// ChatInput.qml
import QtQuick
FocusScope {
id: root
property alias text: input.text
signal accepted(string text)
width: 240
height: 32
Rectangle {
anchors.fill: parent
color: '#000'
border.color: '#fff'
border.width: 2
}
TextInput {
id: input
anchors.left: parent.left
anchors.right: parent.right
anchors.verticalCenter: parent.verticalCenter
anchors.leftMargin: 4
anchors.rightMargin: 4
color: '#fff'
focus: true
onAccepted: function () {
root.accepted(text)
}
}
}When the web socket receives a message it appends the message to the chat view. Same applies for a status change. Also when the user enters a chat message a copy is appended to the chat view on the client side and the message is sent to the server.
// ws_client.qml
import QtQuick
import QtWebSockets
Rectangle {
width: 360
height: 360
color: '#000'
ChatView {
id: box
anchors.left: parent.left
anchors.right: parent.right
anchors.top: parent.top
anchors.bottom: input.top
}
ChatInput {
id: input
anchors.left: parent.left
anchors.right: parent.right
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
focus: true
onAccepted: function(text) {
print('send message: ' + text)
socket.sendTextMessage(text)
box.append('>', text)
text = ''
}
}
WebSocket {
id: socket
url: "ws://localhost:3000"
active: true
onTextMessageReceived: function (message) {
box.append('<', message)
}
onStatusChanged: {
if (socket.status == WebSocket.Error) {
box.append('#', 'socket error ' + socket.errorString)
} else if (socket.status == WebSocket.Open) {
box.append('#', 'socket open')
} else if (socket.status == WebSocket.Closed) {
box.append('#', 'socket closed')
}
}
}
}You need first run the server and then the client. There is no retry connection mechanism in our simple client.
Running the server
cd ws_server
node server.js
Running the client
cd ws_client
qml ws_client.qml
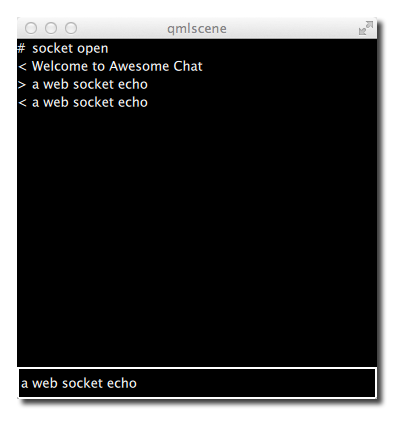
When entering text and pressing enter you should see something like this.
